Understanding Abdominal Hysterectomy and Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy: A Comprehensive Guide
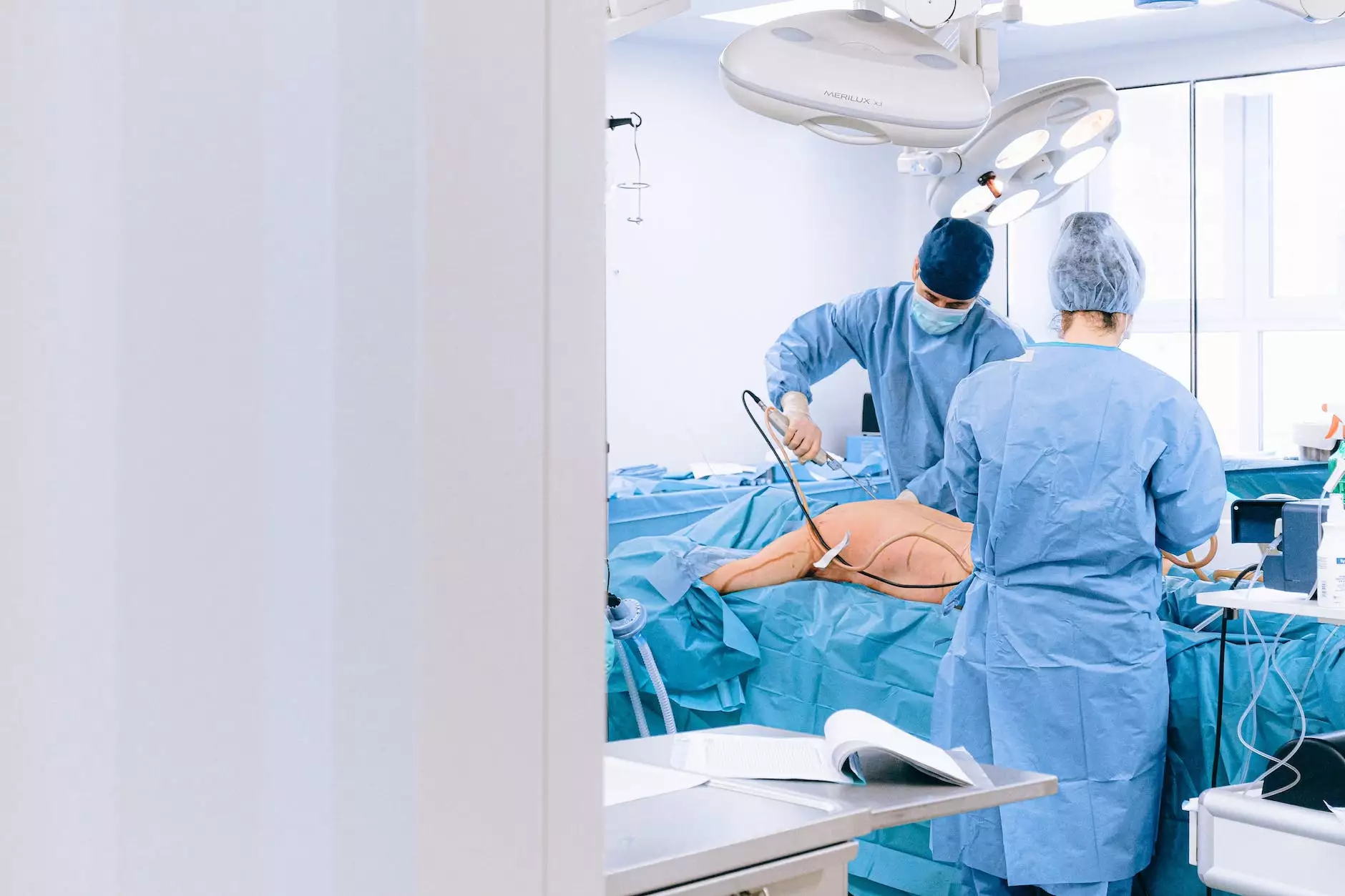
In the realm of women's health, the terms abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy are essential for understanding surgical options. These procedures are often considered for various medical conditions and can significantly impact a woman’s health and quality of life. This article delves deeply into these procedures, covering everything from indications and preparation to recovery and potential complications.
What is an Abdominal Hysterectomy?
An abdominal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus through an incision made in the lower abdomen. This surgery is typically performed when other treatment options for gynecological issues, such as fibroids, endometriosis, or cancer, are deemed insufficient.
Indications for Abdominal Hysterectomy
- Uterine Fibroids: Noncancerous growths that can cause severe pain or heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus.
- Uterine Prolapse: When the uterus slips from its normal position into the vaginal canal.
- Cancer: Malignancies of the uterus, ovaries, or cervix may necessitate this surgery.
What is Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy?
A bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of both the ovaries and the fallopian tubes. This procedure is typically performed alongside a hysterectomy, but it can also be done independently.
Indications for Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy
- Ovarian Cancer: Removal of ovaries is crucial for cancer treatment.
- Genetic Factors: Women with BRCA gene mutations may opt for this surgery to reduce breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Severe Endometriosis: Removing affected ovaries can relieve pain and prevent further complications.
Procedure Overview
Both procedures can be conducted in several ways. The choice of method often depends on the patient’s overall health, the specific conditions being treated, and the surgeon's expertise.
Types of Surgical Approaches
- Open Surgery: The abdomen is opened with a larger incision, providing direct access to the uterus and ovaries. This method may be used for more complex conditions.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a camera, leading to quicker recovery times.
Preparing for Surgery
Preparation for an abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy typically involves several steps:
- Undergoing a thorough medical evaluation, including lab tests and imaging studies.
- Consulting with your healthcare provider to discuss medications and any potential lifestyle changes.
- Arranging for postoperative support, as recovery might require assistance at home.
The Surgical Experience
The actual surgery usually takes about 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the case. Anesthesia is administered, and the patient will be monitored throughout the procedure.
Post-Operative Recovery
Recovery from these procedures can vary significantly among individuals. It is crucial to follow postoperative care instructions to encourage a smooth recovery. Here are some common aspects of recovery:
Hospital Stay
Most patients will stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days following surgery, depending on their specific circumstances and type of procedure performed.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
It is normal to experience some pain following surgery. Pain management typically involves:
- Pain Medications: Prescribed medications will help manage discomfort.
- Rest: Adequate rest is vital to recovery.
- Gradual Activity Increase: Begin with light activities as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Returning to Daily Activities
Patients are often advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks post-surgery. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for a timely return to daily activities.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, both an abdominal hysterectomy and a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy carry potential risks. Some of these include:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the incision site or internally.
- Bleeding: Hemorrhaging may occur, requiring additional interventions.
- Anesthesia Risks: Reactions to anesthesia can occur, particularly in individuals with existing health issues.
- Long-term Effects: Changes in hormonal balance or psychological effects may occur, especially if both ovaries are removed.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Surgeon
Taking the time to choose the right healthcare provider is crucial when considering an abdominal hysterectomy and/or a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Look for a surgeon who specializes in gynecological surgery, has experience with these specific procedures, and has a good track record of patient outcomes.
Post-Surgical Support and Resources
After surgery, it's vital to have support, whether from family, friends, or professional counselors. Many organizations and resources are available to help women navigate this journey:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have gone through similar experiences can be beneficial.
- Health Information Resources: Websites and literature that provide detailed information on healing and recovery.
- Counseling Services: Professional support to help cope with emotional aspects after surgery.
Conclusion
In summary, an abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy are significant surgical interventions that can greatly improve the health and quality of life for many women. Understanding these procedures, their benefits, risks, and recovery processes is crucial for informed decision-making. Always discuss your condition and treatment options with a qualified healthcare professional. For more information, feel free to visit drseckin.com, where you can find expert insights on women's health and personalized care options.
abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo oophorectomy